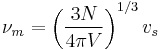Debye frequency
The Debye frequency of a crystal is a theoretical maximum frequency of vibration for the atoms that make up the crystal [1]. It was proposed by Peter Debye as part of the Debye model. It is generally not the same as the actual maximum oscillation frequency for the crystal, due to approximations in the model, however it is still a useful quantity [2]. It plays a role in the computation of the specific heat capacity of solids and in theoretical estimates of rates of diffusion. It is related to the speed of sound (vs) in the crystal and the number density of the crystal 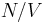 as follows [3]:
as follows [3]: